Parallel Scan
Taskflow provide template methods that construct tasks to perform parallel scan over a range of items.
Include the Header
You need to include the header file, taskflow/algorithm/scan.hpp, for creating a parallel-scan task.
#include <taskflow/algorithm/scan.hpp>
What is a Scan Operation?
A parallel scan task performs the cumulative sum, also known as prefix sum or scan, of the input range and writes the result to the output range. Each element of the output range contains the running total of all earlier elements using the given binary operator for summation.
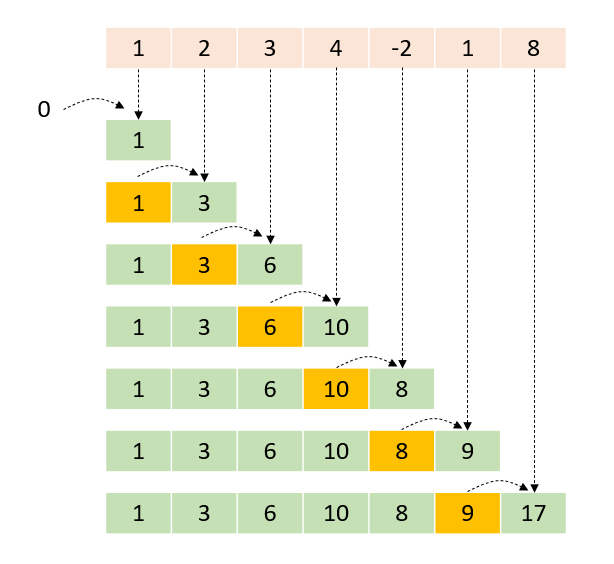
Create a Parallel Inclusive Scan Task
tf::
std::vector<int> input = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; std::vector<int> output(input.size()) taskflow.inclusive_scan( input.begin(), input.end(), output.begin(), std::plus<int>{} ); executor.run(taskflow).wait(); // output is {1, 3, 6, 10, 15}
The output range may be the same as the input range, in which the scan operation is in-place with results written to the input range. For example, the code below performs an in-place inclusive scan over five elements:
std::vector<int> input = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; taskflow.inclusive_scan( input.begin(), input.end(), input.begin(), std::plus<int>{} ); executor.run(taskflow).wait(); // input is {1, 3, 6, 10, 15}
Similar to tf::init. For example, the code below performs an inclusive scan over five elements plus an initial value:
std::vector<int> input = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; std::vector<int> output(input.size()); // performs inclusive scan with an initial value taskflow.inclusive_scan( input.begin(), input.end(), output.begin(), std::plus<int>{}, -1 ); executor.run(taskflow).wait(); // output is {0, 2, 5, 9, 14}
Create a Parallel Transform-Inclusive Scan Task
You can transform elements in the input range before running inclusive scan using tf::
std::vector<int> input = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; std::vector<int> output(input.size()); taskflow.transform_inclusive_scan( input.begin(), input.end(), output.begin(), std::plus<int>{}, [] (int item) { return -item; } ); executor.run(taskflow).wait(); // output is {-1, -3, -6, -10, -15}
You can also associate the transform-inclusive scan with an initial value using tf::uop, i.e., the initial value init does not participate in uop.
std::vector<int> input = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; std::vector<int> output(input.size()); taskflow.transform_inclusive_scan( input.begin(), input.end(), output.begin(), std::plus<int>{}, [] (int item) { return -item; }, -1 ); executor.run(taskflow).wait(); // output is {-2, -4, -7, -11, -16}
Create a Parallel Exclusive Scan Task
tf::
std::vector<int> input = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; std::vector<int> output(input.size()) taskflow.exclusive_scan( input.begin(), input.end(), output.begin(), -1, std::plus<int>{} ); executor.run(taskflow).wait(); // output is {-1, 0, 2, 5, 9}
The output range may be the same as the input range, in which the scan operation is in-place with results written to the input range. For example, the code below performs an in-place exclusive scan over five elements with an initial -1:
std::vector<int> input = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; std::vector<int> output(input.size()); taskflow.exclusive_scan( input.begin(), input.end(), output.begin(), -1, std::plus<int>{} ); executor.run(taskflow).wait(); // output is {-1, 0, 2, 5, 9}
Create a Parallel Transform-Exclusive Scan Task
You can transform elements in the input range before running exclusive scan using tf::
std::vector<int> input = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; std::vector<int> output(input.size()); taskflow.transform_exclusive_scan( input.begin(), input.end(), input.begin(), -1, std::plus<int>{}, [](int item) { return -item; } ); executor.run(taskflow).wait(); // output is {-1, -2, -4, -7, -11}